Actin Filaments Are Anchored to Structures Called
Tap card to see definition. These are the dark-colored A bands which contain thick myosin filaments and the I bands which have a lighter color and contain only thin actin filaments.

10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
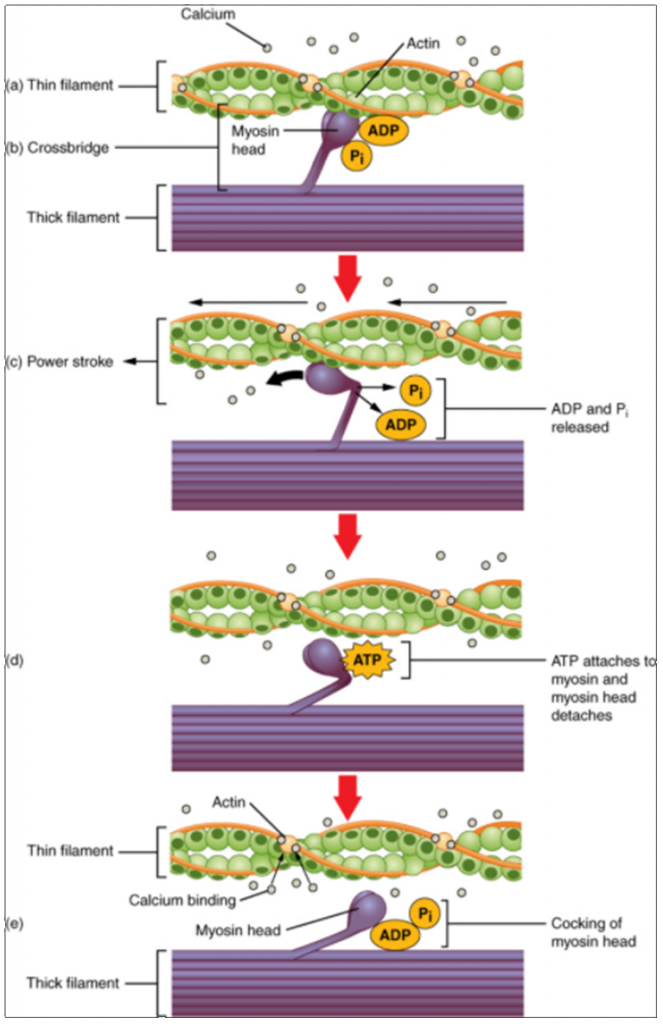
The sliding filament theory explains how actin and myosin interact to contract.

. The cytoskeleton is the skeleton of the cell and is responsible for giving structure and support to the cell. Myofibrils are made of sarcomeres. Similar to focal adhesions and podosomes invadopodia are cell-matrix adhesion sites.
Intermediate filaments as their name suggests are mid-sized with a. Actin fibers or F-actin one of the major components of the cell cytoskel-eton are assembled from protein sub-units called G-actin. Instead they appear to play basically a.
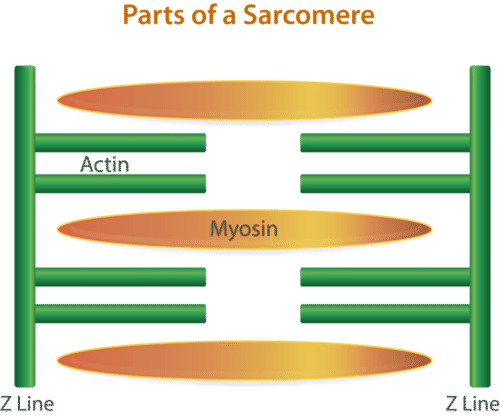
In vertebrate muscles sarcomeric actin filaments are anchored to attachment points called Z-disks which are linked to the extra-cellular matrixECM by a muscle specific focal adhesion site called the costamere. Myosin filaments overlap the actin filaments. The thin actin filaments are anchored to structures called Z lines.
When the sarcomeres contract each of these giant muscle cells shortens and the overall effect is the contraction of the entire muscle. The monomer is a globular protein called G-actin with a molecular weight of 41800 Da. Each sarcomere contains two protein filaments.
Bundles of muscle fibers bound by perimysium. Anchored at their endpoints to. The region from one _ to another is called a _.
The myosin filaments are anchored at the M line in the middle of the sarcomere. Actin filaments are aligned at both ends of the sarcomere and are anchored at the _____ six three ___actin filaments surround each myosin filament and each actin filament is surrounded by ___ myosin filaments. Intermediate filaments have a diameter of about 10 nm which is intermediate between the diameters of the two other principal elements of the cytoskeleton actin filaments about 7 nm and microtubules about 25 nm.
The key difference between actin filaments and microtubules is that actin filaments are the smallest type of filamentous proteins made from actin while microtubules are the largest type of filamentous proteins made from tubulin. They help pistonlike structures called sarcomeres expand and contract. Actin filaments are the smallest type with a diameter of only about 6 nm and they are made of a protein called actin.
Thin actin filaments are anchored at the endpoints to a structure called the _. The myosin and actin filaments overlap in peripheral regions of the A band whereas a middle region called the H zone contains only myosin. As well as binding cells together and helping them migrate the fibers play a major role in the contraction of muscles.
Actin filaments are present in most cells but are especially abundant in muscle cells. One of two proteins that make up a myofibril. Each muscle is surrounded by connective.
In contrast to actin filaments and microtubules the intermediate filaments are not directly involved in cell movements. The region from one Z line to the next makes up one sarcomere. The area where only actin is present is known as the band.
The actin and myosin filaments are organized into repeating units called sarcomeres which can be seen in Figure above. Skeletal muscles are composed of bundles of many long muscle cells. I bands and they are bisected by a Z disc to which actin and elastic filaments are anchored.
When each end of the myosin thick filament moves along the actin filament the two actin. G-actin polymerizes noncovalently into actin filaments called F-actinActin filaments consist of two strands of globular molecules twisted into a helix with a repeat distance of about 36 nm. Myosin or the thick filament is anchored to the M line.
It is an important. The actin filaments are attached at their plus ends to the Z disc which includes the crosslinking protein α-actinin. In thisreview we focus on the dense body of the animal model Caenorhabditis elegans.
The actin filaments are attached to the Z disc whereas the myosin filaments are anchored to a region in the middle of the sarcomere called the M line. They have tiny structures called cross bridges that attach to the actin filaments. Actin also known as the thin filament is anchored into place by structure called a Z disc.
Where myosin filaments anchor to each other in the center of the sarcomere H-zone Z-line. Click card to see definition. The region between two Z lines is the sacromere.
The area where myosin is present is known as the A band. Describe a muscle fiber. The thin actin filaments and the thick myosin filaments are organized in a structure called the sarcomere which shortens as the filaments slide over one another.
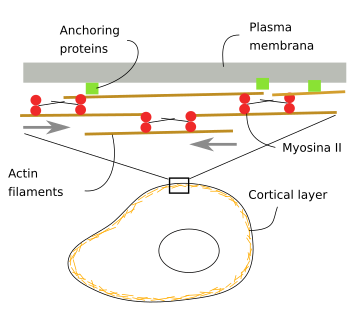
Actin filaments are anchored to structures called Z lines. The invasiveness of cells is correlated with the presence of dynamic actin-rich membrane structures called invadopodia which are membrane protrusions that are associated with localized polymerization of sub-membrane actin filaments.
Muscle Contraction Ck 12 Foundation

Model Of Smooth Muscle Contraction In Smooth Muscle Cells Actin Download Scientific Diagram

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary

What Are Intermediate Filaments Mbinfo

Muscular System How Does A Muscle Contraction Occur What Action Does Muscle Perform A All Movements Require Contraction Of Muscles B 3 Types Of Ppt Download

Anchoring Junction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Skeletal Muscle Sliding Filament Theory Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Physiology

Skeletal Muscle Microscopic Anatomy Ppt Download

Anchoring Junction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Muscular System How Does A Muscle Contraction Occur What Action Does Muscle Perform A All Movements Require Contraction Of Muscles B 3 Types Of Ppt Download
9 3 Muscle Fibre Contraction And Relaxation Fundamentals Of Anatomy And Physiology

Sarcomere An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Actin Filament An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology I
The Cell 7 Cytoskeleton Actin Filaments Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




Comments
Post a Comment